Reference
The INTERLIS 2 reader and writer module (ili2fme) provides FME with access to INTERLIS 2 and INTERLIS 1 transfer files.
This documentation assumes you are familiar with FME and the INTERLIS 1 and 2 formats. For more information about FME, please read the FME documentation. For more information about INTERLIS, go to https://www.interlis.ch/.
Reader Parameters
- Models
-
The required INTERLIS models to read the dataset (the model name, not the file of the model; so no extension .ili) and separated by semicolons (;). The default value %DATA is a placeholder and means that models are determined by inspecting the transfer file.
- Models Directory
-
This is the folder that contains the .ili files. These files are scanned for INTERLIS models. You may use %XTF_DIR as a placeholder for the folder of the data file that you will read. Also model repositories might be specified (such as http://models.interlis.ch/). Multiple folders or repositories may be separated by semicolons (;).
- Topics Filter
-
These are the qualified names of INTERLIS topics to read (for example, DM01.Bodenbedeckung). You can enter multiple topic names, separated by semicolons (;). If set, other topics will be ignored.
This parameter can remain empty. If it is not set, all topics will be read.
- Check TID/OID Uniqueness
-
- Yes
-
The reader will check if the TIDs/OIDs are unique.
- No
-
It will bypass this check.
- Validate
-
- Yes
-
The reader will validate the data by using the ilivalidator.
- No
-
It will bypass the validation completely.
- Validate Attribute/Role Multiplicity
-
- Yes
-
The reader will check for mandatory but missing values/references.
- No
-
It will bypass this validation.
- Validator Configuration
-
An ilivalidator configuration file to fine tune the validation. See https://github.com/claeis/ilivalidator/blob/master/docs/ilivalidator.rst#konfiguration for further information.
- Geometry Encoding
-
Defines the encoding of geometry attributes, which are not used as FME geometry (only the first geometry attribute becomes an FME geometry).
- FMEXML
-
encodes as FME XML
- FMEBIN
-
encodes as FME Binary
- FMEHEXBIN
-
encodes as FME Hex Binary
- OGCHEXBIN
-
encodes as OGC Hex Binary
- Mapping of multiple Geometry Attributes
-
Defines the encoding of INTERLIS geometry attributes, in cases where the INTERLIS class defines multiple attributes of type geometry.
- EncodeAsFmeAttribute
-
Only the first geometry attribute becomes an FME geometry. Any additional INTERLIS geometry attributes are mapped to FME attributes.
- RepeatFeature
-
The reader creates multiple FME features for one single INTERLIS object; one feature per geometry attribute value of the single INTERLIS object (any non-geometry attribute is the same in all this cloned features).
- ITF Linetable Mapping
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 1 datasets.
- Polygon
-
The reader will create polygons for all SURFACE/AREA attributes; no linetable features are created. This option requires valid data.
- Raw
-
The reader will read the data as it is in the ITF transfer file. No polygon building for SURFACE/AREA attributes will be done. This option enables to read invalid SURFACE/AREA data, and can be used for error analysis.
- Polygon+Raw
-
The reader will create polygons for all SURFACE/AREA attributes, but will also create linetable features. AREA linetables will contain one or two references to the features with the polygons. This option requires valid data.
- Inheritance Mapping Strategy
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 2 datasets.
NoteFor more information, see the section titled Inheritance mapping strategies under 'Feature Representation' in the Swiss INTERLIS (ili2fme) Reader/Writer section of the Readers and Writers Manual. - SuperClass
-
The superclass inheritance mapping strategy is applied.
- SubClass
-
The subclass inheritance mapping strategy is applied.
- Trim Values
-
- Yes
-
The reader will remove leading and trailing spaces from text attributes.
- No
-
The reader will bypass this data cleaning.
- ITF Add Default Values
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 1 datasets.
- Yes
-
The reader will parse the explanation at the end of attribute definitions that are optional. If there is no attribute value in the data, it will add the one given in the model.
- No
-
The reader will not supply any default values to the data.
- ITF Renumber TIDs
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 1 datasets.
- Yes
-
The reader will renumber the objects so that the TID becomes unique across the whole transfer. Any references to the renumbered objects are changed appropriately.
- No
-
The reader will read the TIDs without making any changes.
- ITF Read enum Values as Code
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 1 datasets.
- Yes
-
The reader will read values of attributes of type enumeration as numeric code (the same code as it appears in the ITF transfer file). This option is not recommended and exists only for backward compatibility reasons.
- No
-
The reader will map the code from the transfer file to enumeration element name (the value as it would appear in an INTERLIS 2 transfer file). This option is recommended because it is less error prone and offers compatibility between INTERLIS 1 and 2.
- Create Feature Types For Enumerations
-
Controls how FME feature types are created for INTERLIS enumerations
- No
-
No feature types are created for enumerations
- SingleType
-
A single additional feature type called "XTF_ENUMS" is created and each element of all enumeration types is provided as a feature of this feature type.
- OneTypePerEnumDef
-
One feature type is created for each enumeration type.
- http Proxy Host
-
This is the proxy server that ili2fme will use to access model repositories.
- http Proxy Port
-
This is the proxy server that ili2fme will use to access model repositories.
- Enable Trace Messages
-
Controls the level of detail of log messages written by the reader.
- Yes
-
details progress messages will be written to the log
- No
-
only normal progress messages will be written to the log
Writer Parameters
- Models
-
The required INTERLIS models to write the dataset (the model name, not the file of the model; so no extension .ili) and separated by semicolons (;). The default value %DATA is a placeholder and means that models are determined by inspecting the features.
- Models Directory
-
This is the folder that contains the .ili files. These files are scanned for INTERLIS models. You may use %XTF_DIR as placeholder for the folder of the data file that you will write. Also model repositories might be specified (such as http://models.interlis.ch/). Multiple folders or repositories may be separated by semicolons (;).
- Check TID/OID Uniqueness
-
- Yes
-
Checks if the TIDs/OIDs are unique.
- No
-
This check is bypassed.
- Validate
-
- Yes
-
The writer will validate the data by using the ilivalidator.
- No
-
It will bypass the validation completely.
- Validate Attribute/Role Multiplicity
-
- Yes
-
The writer will check for mandatory but missing values/references.
- No
-
It will bypass this validation.
- Validator Configuration
-
An ilivalidator configuration file to fine tune the validation. See https://github.com/claeis/ilivalidator/blob/master/docs/ilivalidator.rst#konfiguration for further information.
- Inheritance Mapping Strategy
-
Applies only to INTERLIS 2 datasets.
- SuperClass
-
The superclass inheritance mapping strategy is applied.
- SubClass
-
The subclass inheritance mapping strategy is applied.
- Geometry Encoding
-
Defines the encoding of geometry attributes which are not used as FME geometry (only the first geometry attribute becomes FME geometry).
- FMEXML
-
encodes as FME XML
- FMEBIN
-
encodes as FME Binary
- FMEHEXBIN
-
encodes as FME Hex Binary
- OGCHEXBIN
-
encodes as OGC Hex Binary
- Trim Values
-
- Yes
-
The writer will remove leading and trailing spaces from text attributes.
- No
-
It will bypass this data cleaning.
- Use Linetables
-
This field applies only to INTERLIS 1 datasets with INTERLIS AREA or INTERLIS SURFACE attributes.
- Yes
-
The writer will expect one additional feature type for each INTERLIS SURFACE or AREA attribute. The additional feature type with the suffix _$(attributeName) contains the line helper features as they should appear in the transfer-file.
- No
-
The writer will create the line helper table out of the polygons/donuts.
- http Proxy Host
-
This is the proxy server that ili2fme will use to access model repositories.
- http Proxy Port
-
This is the proxy server that ili2fme will use to access model repositories.
- Enable Trace Messages
-
Controls the level of detail of log messages written out.
- Yes
-
Detailed progress messages will be written to the log.
- No
-
Only normal progress messages will be written to the log.
Feature Representation
The following clauses describe how ili2fme maps INTERLIS objects to FME features. Features written to the INTERLIS transfer file are expected to have the same structure, as they would have had when read.
INTERLIS allows for some nesting of type definitions. A class or table is defined in a topic. Several topics are grouped to a model. FME does not allow such a nesting; therefore, ili2fme maps INTERLIS class with their qualified name to FME feature types.
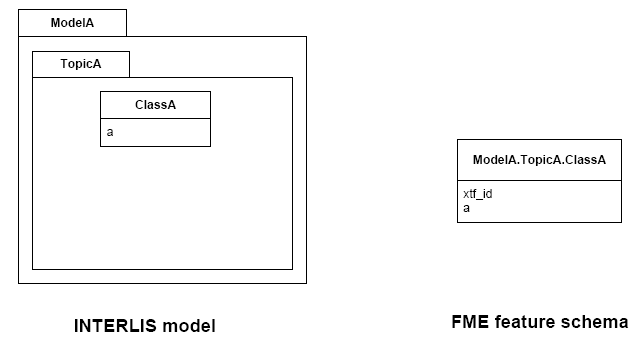
If an INTERLIS 2 data file has multiple baskets (instances of a topic; set of objects) of the same topic or the model has extended topics, additional format attributes are required.
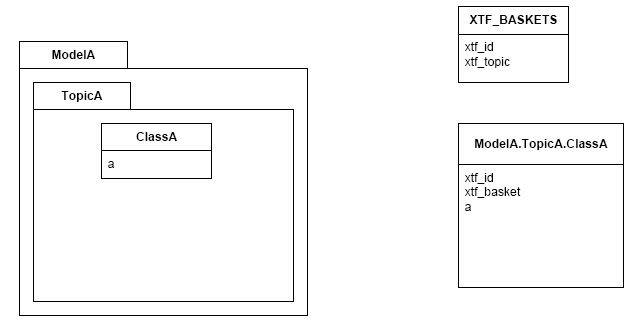
To know which feature belongs to which basket, each feature has a reference to the basket in the format attribute xtf_basket. Each basket is represented as an instance of the format feature type XTF_BASKETS. The attribute xtf_topic holds the qualified topic name that describes this basket (in this case that would be ModelA.TopicA). The attribute xtf_id of the feature type XTF_BASKETS is the transfer identification of the basket (BID).
Multiple Geometries per Class
An INTERLIS class may define multiple attributes of type geometry.
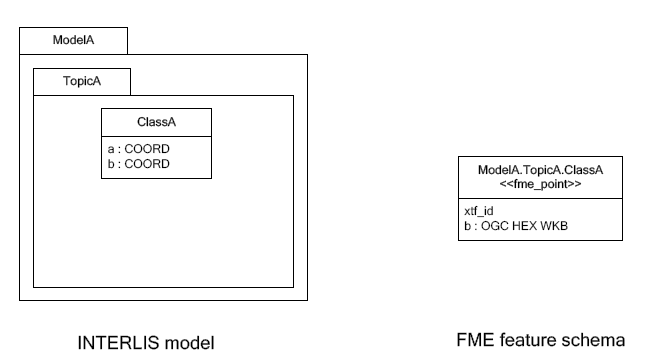
ili2fme maps the first geometry of the INTERLIS class to the FME geometry of the feature. Any additional INTERLIS geometry attributes are mapped to existing FME attributes. The value of these attributes (attribute b in the diagram above) is HEX-encoded OGC WKB (this can be changed with the parameter Geometry Encoding) and can be extracted from that attribute to the feature geometry with the GeometryReplacer transformer or set with the GeometryExtractor transformer.
INTERLIS 1 Area
INTERLIS 1 encodes attributes of type AREA in helper table prior to the main table. ili2fme can read these attributes in three modes:
-
build polygons/donuts automatically from the line table
-
read the main table and the line table as they are in the transfer file
-
combination of the two cases above
Automatic polygon building works only, if the AREA attribute is the first geometry attribute of the INTERLIS table.
With automatic polygon building, the mapping is as follows:
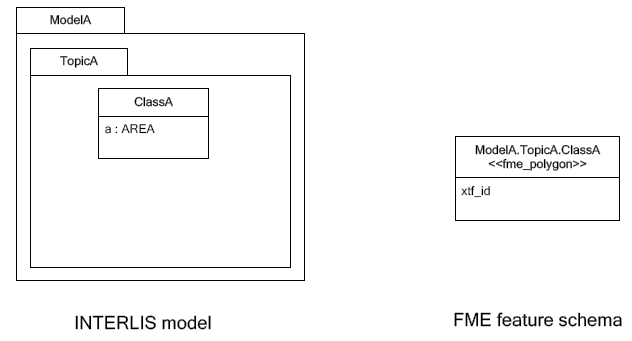
With automatic polygon build disabled, the mapping is as follows:
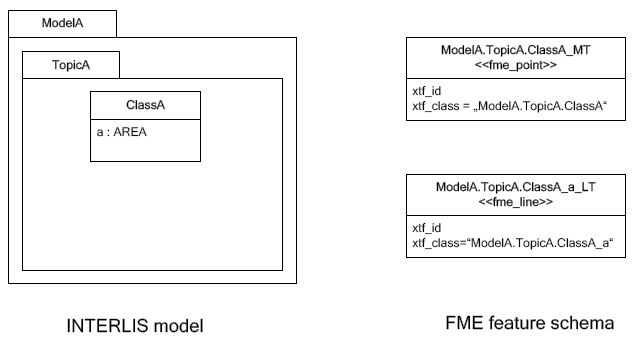
INTERLIS 1 Surface
INTERLIS 1 encodes attributes of type SURFACE in helper table following the main table. ili2fme can read these attributes in three modes:
-
build polygons/donuts automatically from the line table
-
read the main table and the line table as they are in the transfer file
-
combination of the two cases above
Automatic polygon building works only, if the SURFACE attribute is the first geometry attribute of the INTERLIS table.
With automatic polygon building the mapping is as follows:
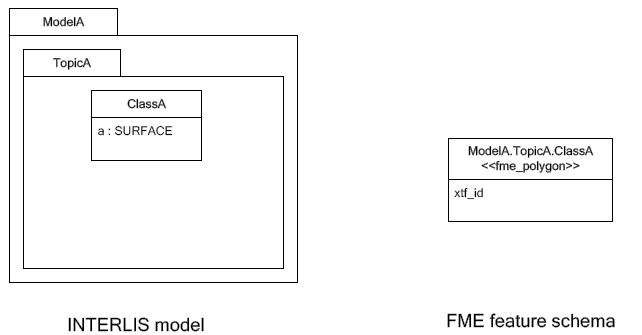
With automatic polygon build disabled, the mapping is as follows:
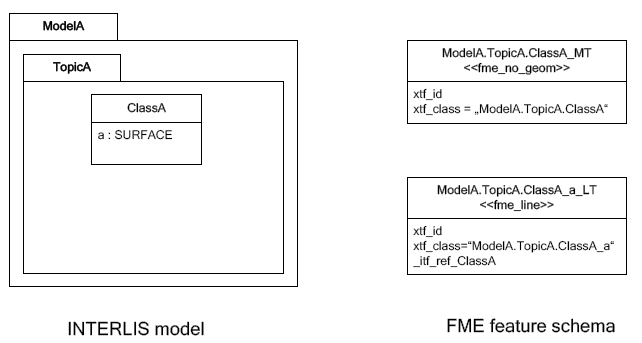
The line table (ModelA.TopicA.ClassA_a_LT) gets an additional
attribute (with the name of the main class; in this case
_itf_ref_ClassA) that is a reference from the lines to the feature in
the main table (ModelA.TopicA.ClassA_MT)
INTERLIS 2 Incremental Transfer
INTERLIS 2 supports incremental transfers (change only transfers). Incremental transfer happens per basket. There are two kind of incremental transfers: INITIAL and UPDATE. INITIAL ist the first transfer in a series of transfers. It includes all objects. UPDATE is used for all succeeding transfers following INITIAL and includes only changed objects since the last transfer. Both kinds require additional format attributes.
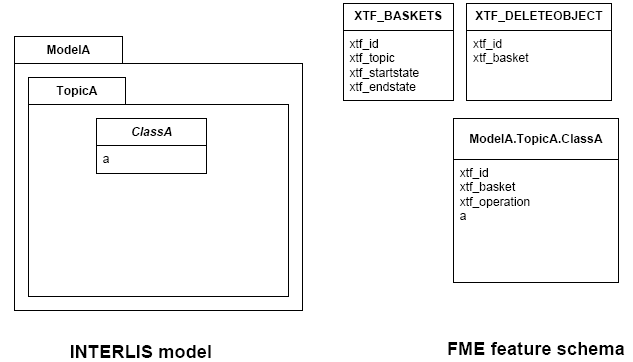
For an INITIAL data transfer, the XTF_BASKETS feature that represents
the basket has a value in the xtf_endstate attribute. The
xtf_startstate attribute should not be set. There are no
XTF_DELETEOBJECT features. The xtf_operation attribute should not be
set.
For an UPDATE data transfer, the XTF_BASKETS feature that represents the
basket has a value in the xtf_startstate and the xtf_endstate
attribute. The xtf_startstate value is the same as the xtf_endstate
of the last transfer of that basket. The xtf_operation attribute
should be set to INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE. Instead of mapping
deleted objects to ordinary features with xtf_operation set to
DELETE, they may alternatively be mapped to instances of the format
feature type XTF_DELETEOBJECT (without any INTERLIS attribute values;
just xtf_id and xtf_basket).
Inheritance Mapping Strategy
ili2fme supports to inheritance mapping strategies. Depending on your INTERLIS model, one or the other is appropriate.
Superclass Strategy
Attributes of non-root classes are shifted to the root, as illustrated by the following figure:
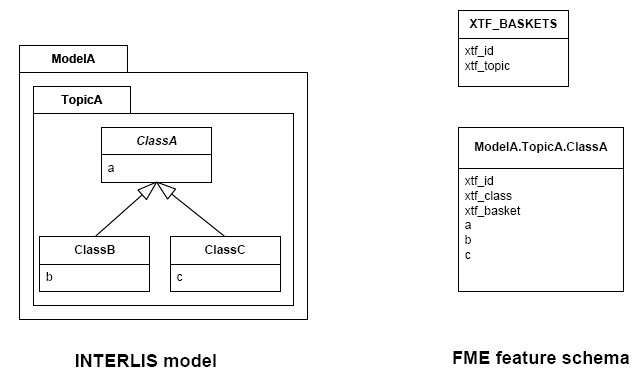
The format attribute xtf_class may be used to determine if a feature
is an instance of class ModelA.TopicA.ClassB or class
ModelA.TopicA.ClassC.
Subclass Strategy
Attributes of base classes are shifted to leafs, as illustrated by the following figure:
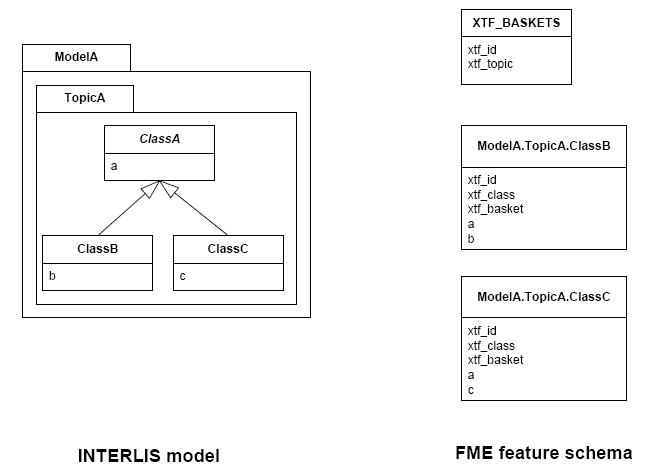
There is no feature type ModelA.TopicA.ClassA because it’s an abstract
class in the INTERLIS model.
Enumerations
There are two modes to read enumerations:
- SingleType
-
will read all elements of all enumerations with the same FME feature type XTF_ENUMS.
- OneTypePerEnumDef
-
will create one FME feature type for each enumeration type.
Enumerations as a Single Feature Type
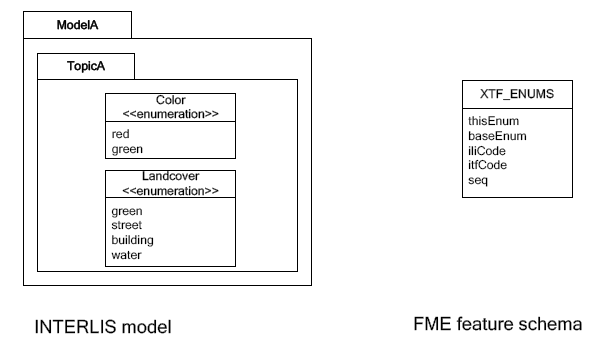
For the feature type XTF_ENUMS, the following features will be read:
| thisEnum | baseEnum | iliCode | itfCode | seq |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ModelA.TopicA.Color |
red |
0 |
||
ModelA.TopicA.Color |
green |
1 |
||
ModelA.TopicA.Landcover |
green |
0 |
||
ModelA.TopicA.Landcover |
street |
1 |
||
ModelA.TopicA.Landcover |
building |
2 |
||
ModelA.TopicA.Landcover |
water |
3 |
The property baseEnum is only defined, if the enumeration is an extended one.
The property seq is only set, if the enumeration is ordered.
One Feature Type per Enumeration
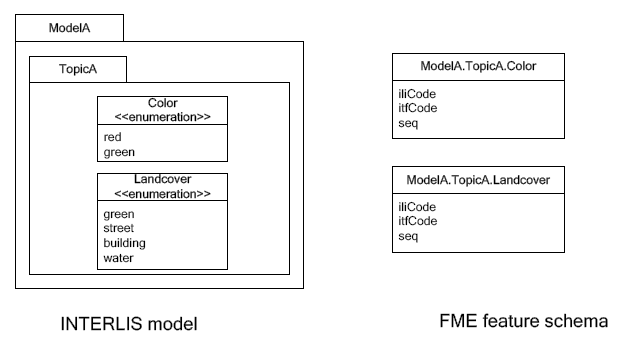
For the feature type ModelA.TopicA.Color the following features will
be read:
| iliCode | itfCode | seq |
|---|---|---|
red |
0 |
|
green |
1 |
BAG/LIST OF
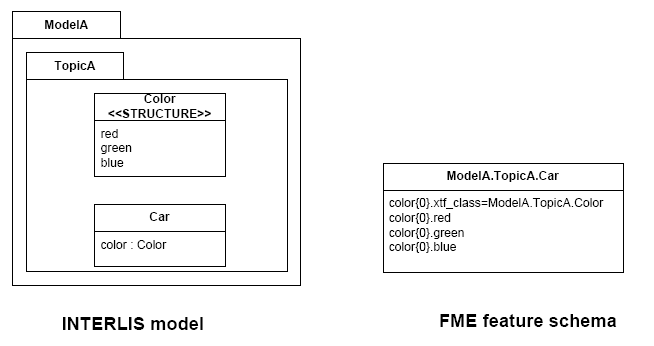
INTERLIS structure attributes (in the example the attribute "color" in
the class "Car") are mapped to FME lists. The definition of the INTERLIS
structure (in the example the structure "Color") is not mapped as a FME
feature type. The type of the structure element is defined by the value
of the attribute xtf_class (similar to the class type of objects; see
sec. Superclass Strategy), which is mandatory to be set. In the example
has the list attribute color{0}.xtf_class therefore the value
ModelA.TopicA.Color.
Format Attributes
In addition to the generic FME feature attributes that FME Workbench adds to all features (see About Feature Attributes), this format also adds format-specific attributes.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
xtf_id |
Value of the TID XML-attribute out of the INTERLIS transfer file. Unique across all feature types. |
xtf_class |
Qualified name of the INTERLIS class name. This is different from the feature type name in the case of non base classes. In the figure above would ModelA.TopicA.ClassB be a possible value. If this value is not set, the feature type name is used as the qualified INTERLIS class name. |
xtf_basket |
Value of the BID XML-attribute out of the INTERLIS transfer file. May be used as foreign key to a feature of the feature type. XTF_BASKET (see below). On writing, this may be used to write multiple baskets of the same topic. If writing INTERLIS 1 transfer files, this attribute is not required. |
xtf_operation |
Only used for incremental INTERLIS 2 transfer. Possible values are: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE. |
xtf_consistency |
Only used for somehow modified data. Not yet fully supported. |
xtf_geomattr |
Deprecated: Name of the geometry attribute read (e.g. "Geometrie"). An INTERLIS class may define multiple geometry attributes. |
Format Features
The reader creates additional feature types, and the writer expects this feature types as well. If writing INTERLIS 1 transfer files, these feature types are not required.
XTF_TRANSFER
Content of the INTERLIS 2 transfer file header section.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
oidspace{} |
Content from the |
oidspace{}.name |
For each OID domain used in this INTERLIS 2 transfer file, an alias name (as used in this transfer file). |
oidspace{}.oiddomain |
Qualified name of the INTERLIS 2 OID domain definition. |
comment |
Content of |
XTF_BASKETS
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
xtf_id |
For each basket in the INTERLIS 2 transfer file, the value of
the |
xtf_topic |
Qualified name of the INTERLIS 2 topic name. In the figure
above would |
xtf_startstate |
Only used for incremental INTERLIS 2 transfer. If set,
it indicates an |
xtf_endstate |
Only used for incremental INTERLIS 2 transfer. If set, it indicates an incremental transfer. If it is not set, this is not an incremental transfer. |
xtf_consistency |
Only used for somehow modified data. Not yet fully supported. |
XTF_DELETEOBJECT
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
xtf_id |
Value of the |
xtf_basket |
Value of the |
XTF_ENUMS
This feature type is only created by the reader if the parameter Create Feature Types For Enumerations is set to SingleType.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
thisEnum |
Qualified INTERLIS name of the enumeration definition of this element. |
baseEnum |
Qualified INTERLIS name of the base enumeration definition of
this element. This is only set, if the enumeration is |
iliCode |
Qualified INTERLIS Name of the enumeration element. Same as it would appear in an INTERLIS 2 transfer file (XTF). |
itfCode |
Code of the enumeration element as it would appear in an INTERLIS 1 transfer file (ITF). |
seq |
Ordering position of the element. Only set, if this enumeration is
|
XTF_ERRORS
Errors from the reader.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
iliname |
Qualified name of the INTERLIS 2 model element that is related to the message |
message |
Error message |
tid{} |
|
Limitations
-
custom line forms
-
XTF line attributes
-
recursive structure attributes
License
-
ili2fme is licensed under the LGPL (Lesser GNU Public License).
-
Some libraries used by ili2fme are licensed under MIT/X.
-
Some libraries used by ili2fme are licensed under Apache 2.0.
-
Some libraries used by ili2fme are licensed under a library specific license.
-
ili2fme includes software developed by The Apache Software Foundation (http://www.apache.org/).
Installation
|
Note
|
|
Requirements
For the current version of ili2fme, you will need a JRE (Java Runtime Environment) installed on your system, version 1.6.0 or later. The JRE (Java Runtime Environment) can be downloaded for free from the Website http://www.java.com/.
Files
To install ili2fme, choose a directory and extract the distribution file there.
Copy the files and subdirectories of ${ili2fme}/FME Suite to your FME directory.
Add your standard INTERLIS models to the directory ${FME}/plugins/interlis2/ilimodels.
At runtime, ili2fme requires the following files:
${FME}/plugins/ili2c.jar
${FME}/plugins/ili2fme.jar
${FME}/plugins/jts-core-1.14.0.jar
${FME}/metafile/ch.ehi.fme.Main.fme
${FME}/formatsinfo/interlis2.db
Configuration
To use ili2fme with the FME Universal Viewer, FME requires you to set an environment variable: FME_VIEWER_THREADING=SINGLE.
ili2fme doesn’t use or require any windows registry entries or user settings file.
How to migrate/update an existing ili2fme installation
Just copy the files and subdirectories of the new ${ili2fme}/FME Suite to your FME directory.
Starting with ili2fme version 4.0, there is no longer a native part required.
You may delete the files iom_fme.dll and xerces-c_2_6-interlis2.dll (from previous ili2fme versions).
You must delete the file jts-1.8.jar and jts-1.13.jar. They are in conflict with jts-core-1.14.0.jar
and result in a error
tried to access field com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.LineString.points from class ch.interlis.iom_j.itf.impl.jtsext.geom.CompoundCurveRing